1 MB
Key Takeaways
- High Economic Growth: Military aid to Ukraine brings economic benefits to the US, with about 90% of aid funds going directly to American companies and workers.
- Updating the US Military Arsenal: By sending Ukraine refurbished or modernized models of old equipment, the US is fully re-equipping its defense stocks. It solves the problem of old equipment disposal.
- Profit Growth for Leading Military Manufacturers: The four giants in the US arms manufacturing sector have confirmed financial growth in 2022-2023. It improved the military image among partners and competitors.
- Republicans Deliberately Ignore Well-Known Indicators: At least 31 Republican senators and members of Congress whose states receive economic benefits from aid to Ukraine voted against or tried to limit this aid due to party politics.

It is widely believed that the ongoing war in Ukraine is a costly and unpromising prospect for the US economy. Supporting Ukraine involves significant financial costs, especially in the military sphere, given the need for regular packages of equipment and heavy machinery. Many believe it not only negatively affects the US arsenal itself, reducing the country’s defense capability, but also calls into question its ability to fulfill its obligations to protect.
The thesis is quite convincing as there is no doubt that the war brings only losses. However, victory in the war and regular support provide potential benefits with long-term geopolitical consequences.
Given the above considerations, this paper will analyze the current situation in the US, the cost of aid to Ukraine, and the potential benefits to understand whether these costs are a financial burden or an investment opportunity.
The Cost of Military Aid to Ukraine
The US economy is currently facing inflationary pressure, and the Federal Reserve is raising interest rates to combat this. While a downturn may be on the horizon, the overall economic situation remains relatively strong. However, public opinion on foreign aid can be influenced by domestic issues. Moreover, Republicans are pursuing a fairly active opposition policy, which often complicates and delays the process of providing assistance, which will be discussed further below.
As of October 2023, the US has provided Ukraine with about $44 billion in military aid since the start of the invasion.
This is a significant amount that, at first glance, can have an extremely negative impact on the US defense capability and its financial position. However, according to the data provided by the Ukraine Support Tracker database of military, financial, and humanitarian aid to Ukraine, this figure does not exceed 0.199% of the US GDP and is also only a significantly smaller part of the annual budget that Congress allocates to the Department of Defense. For example, in 2023, this amount was $816.7 billion.
Benefits for the US
When the United States spends money on the purchase of military equipment within the framework of an international aid package, the equipment may go abroad, but the money and jobs remain in America. For ordinary American workers, this can mean permanent employment and stable income, and for industrial enterprises and companies engaged in the manufacture of military equipment – new grants, federal funding, and business expansion.
According to The Washington Post, almost 90% of the funds that Congress allocates for military aid to Ukraine remains directly in the US and manifests itself in financing its own production. Also, as indicated in the article, most of the equipment that is transferred to Ukraine is refurbished or modernized old models, and new production replaces the equipment sent to the front, thus updating stocks and strengthening the US military capability.
The profits from such a policy can be seen with the naked eye. The leading companies engaged in the production of weapons and heavy equipment achieved extraordinary growth rates in 2022. With the exception of the decline in Boeing’s market value due to predicted “supply chain problems,” the other four companies in the “Big Five” grew by more than $10 billion in annual market value.

Also, with the exception of Boeing, the four aforementioned giants performed well in the stock market in 2022.
Furthermore, it is important to highlight that the law, prepared by Congress in cooperation with the Joe Biden administration regarding the establishment of the budget for the Department of Defense for the year 2023, fully offsets inflation with additional payments. The law provides for a 4.6 percent increase in salaries for military and civilian personnel of the department, as well as allocates an additional $45 billion, more than originally proposed, to counteract the effects of inflation and accelerate the implementation of the National Defense Strategy. Additionally, new special incentives have been introduced for military personnel in career qualification fields.
Regarding personnel, the law allows for additional funding to mitigate the impact of inflation on compensations. It also introduces wording that allows a greater number of military personnel to qualify for basic needs assistance by increasing the threshold of eligibility and the amount of assistance from 130 percent of the federal poverty line to 150 percent. The law authorizes the Secretary of Defense to increase this assistance to 200 percent of the poverty line when necessary.
the HIMARS production line in Camden,
Ark. (Jen Judson/Staff)
In 2023, defense manufacturing companies also showed good results. For example, Lockheed Martin, the manufacturer of HIMARS, which plays a central role in the counteroffensive in Ukraine, plans to increase its workforce at its Camden, Arkansas plant by 20% and recently announced an increase in profits by the end of the year. Similarly, General Dynamics has committed to building new manufacturing facilities in Mesquite, Texas. It is expected to employ at least 125 people, provide business opportunities for local suppliers, retailers, and restaurants, and potentially help transform the area into an industrial hub of well-paying jobs. Such changes occur only when the Pentagon sends strong and stable market signals to the defense industry, providing it with confidence for expansion and hiring.
Northrop Grumman’s sales in the third quarter of the Defense Systems segment grew by 6% due to the high demand for ammunition and rocket engines used in Multiple Launch Rocket Systems (MLRS), which play a crucial role in supporting Ukraine’s defense efforts against Russian forces.
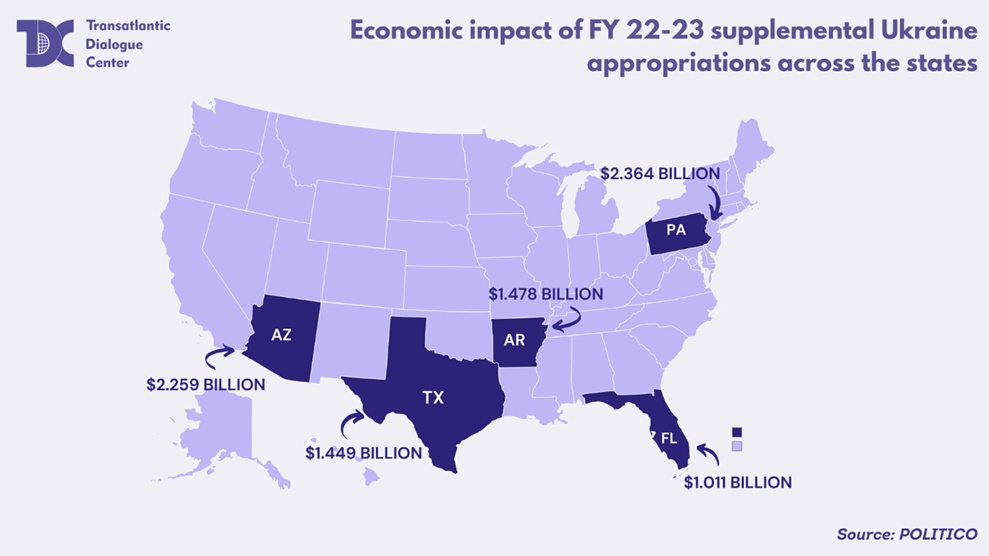
As for each state’s revenue, significant shifts can be seen for the years 2022-2023. According to a map obtained by Politico, Pennsylvania received $2.364 billion in investments for the production of ammunition and tactical vehicles for Ukraine, the most among other states. Meanwhile, Arizona ranks second with $2.259 billion. Texas and Arkansas received $1.449 billion and $1.478 billion, respectively, and Florida received $1.011 billion. According to the chart, states received a total of over $27 billion in investments from Ukraine’s armaments.
On December 14, 2023, a meeting of Congress was held regarding the planning of the new defense budget for the year 2024. A bill on the United States defense policy (NDAA) amounting to a record $886 billion was adopted, which also allows for a 5.2% increase in salaries for military and civilian personnel.
Republicans’ Position
A faction of the Republican Party, largely aligned with former President Donald Trump, has expressed concerns regarding the cost and sustainability of aid to Ukraine. These concerns were most vividly demonstrated in the blocking of a $50 billion aid package in September 2023, which was later approved with amendments.
American media outlets have repeatedly reported that due to internal political disagreements among major political forces, Congress was compelled to postpone decisions on a new aid package proposed by President Joe Biden.
Considering all the aforementioned benefits for U.S. military production, there should be no doubts among Republican senators and state representatives about the economic benefits resulting from the revival of production. However, as of February 2024, a new aid package has not been passed.
When Ohio Senator Jay D. Vance joined a picket line of the United Auto Workers at the Jeep assembly plant in Toledo in October, he stated that he wanted to “demonstrate some support for UAW workers” in his state. However, he did not show the same solidarity with UAW workers in Lima, Ohio, who produce Abrams tanks and Stryker combat vehicles for Ukraine through military aid approved by Congress. Vance opposes aid to Ukraine, as does Congressman Jim Jordan, whose constituency includes Lima.
Ohio voters could expect their elected leaders to push the Biden administration to provide more tanks and vehicles produced in Lima to Ukraine or to demand that more of them be included in the aid package to Ukraine, which Congress will soon consider. Instead, Vance and Jordan are fighting to ensure that Ukraine no longer receives tanks and combat vehicles from the only tank plant in America.
They are not alone. In total, 31 senators and House members whose states or districts benefit from funding for Ukraine voted against or restricted this aid. Among them are some of the most prominent anti-Ukrainian voices in Congress, such as Republican senators Josh Hawley (Missouri), Tommy Tuberville (Alabama), and Mike Braun (Indiana), as well as Republican representatives Matt Gaetz (Florida), Bill Posey (Florida), Anna Paulina Luna (Florida), and Lance Gooden (Texas).
If, for the United States, this issue is a matter of postponement or a conscious refusal of state funding for national production, as has been demonstrated previously, then from Ukraine’s perspective, the situation becomes even more discouraging. The absence of arms supplies for over a month negatively affects the physical ability of Ukraine’s Armed Forces to conduct counteroffensives and defend against the aggressor.
Conclusions
In conclusion, U.S. military aid to Ukraine is an investment opportunity, not a financial burden for America. While the financial cost of aid to Ukraine is undeniable, the potential benefits extend far beyond immediate geopolitical considerations or the struggle for hegemony in the region. The absolute dollar amounts may seem significant but are modest in the context of the U.S. defense budget and economy. Aid to Ukraine contributes to growth, job creation, and income for American defense contractors and industry workers. For businesses and ordinary American workers, it means stable income, steady employment, and commercial development.
However, partisan opposition remains a hindrance, as some Republican lawmakers prioritize politics over the economic benefits that military support for Ukraine provides to their constituents. Continuing aid to Ukraine is strategically, morally, and economically the right policy for the United States.
Disclaimer: The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in the papers published on this site belong solely to the authors, and not necessarily to the Transatlantic Dialogue Center, its committees, or its affiliated organizations. The papers are intended to stimulate dialogue and discussion and do not represent official policy positions of the Transatlantic Dialogue Center or any other organizations the authors may be associated with
